Global Positioning System (GPS) technology has revolutionized navigation, mapping, and surveying. Among the latest advancements in GPS technology is Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) GPS, which offers centimeter-level accuracy. If you are new to this technology, A Beginner’s Guide to rtk gps Systems and Applications will help you understand its basics, benefits, and practical uses.
What is RTK GPS?
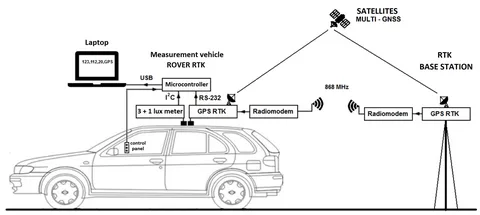
RTK GPS is an advanced GPS technology that enhances standard GPS positioning. Traditional GPS systems usually provide accuracy within a few meters, which is sufficient for navigation but not for precision tasks. RTK GPS, however, uses a base station and a rover to correct errors in real time, allowing for highly accurate positioning—often within 1–2 centimeters.
The system works by transmitting correction data from the base station to the rover via radio, cellular networks, or other communication links. This real-time correction significantly reduces errors caused by satellite geometry, atmospheric conditions, and clock inaccuracies.
Key Components of RTK GPS Systems
Understanding the components of an RTK GPS system is crucial for beginners:
- Base Station: A stationary GPS receiver placed at a known location. It calculates errors in the satellite signals and transmits corrections.
- Rover Receiver: A mobile GPS receiver that receives correction data from the base station, providing precise position measurements.
- Communication Link: The medium that transmits corrections from the base station to the rover, such as radio signals, mobile networks, or the internet.
- Software Tools: Applications for data collection, processing, and analysis. These tools help integrate RTK GPS data into practical workflows like mapping or construction.
Applications of RTK GPS
The versatility of RTK GPS systems makes them valuable across various industries:
- Agriculture: Precision farming benefits from RTK GPS by enabling accurate planting, fertilization, and harvesting.
- Construction: RTK GPS ensures precise measurements for site layouts, earthworks, and infrastructure projects.
- Surveying and Mapping: Surveyors use RTK GPS for accurate land measurements and topographic mapping.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Self-driving cars and drones utilize RTK GPS for navigation and positioning with high precision.
Advantages of Using RTK GPS
- High Accuracy: RTK GPS reduces positioning errors from meters to centimeters.
- Real-Time Data: Corrections are applied instantly, making it ideal for time-sensitive operations.
- Cost-Effective in the Long Run: Although initial costs may be high, the accuracy reduces rework and increases efficiency.
- Versatile Applications: RTK GPS can be used in agriculture, construction, surveying, marine navigation, and more.
Getting Started: A Beginner’s Perspective
For beginners, starting with RTK GPS involves:
- Learning the terminology: base station, rover, correction signals.
- Choosing the right equipment: select receivers compatible with your intended applications.
- Understanding software integration: most RTK systems include mapping or survey software.
- Practicing in controlled environments: start with small projects to understand signal behavior and error correction.
By following these steps, beginners can gradually become proficient in using RTK GPS systems for precise applications.
Conclusion
A Beginner’s Guide to RTK GPS Systems and Applications shows that RTK GPS is not only a cutting-edge technology but also an essential tool for industries that require precise positioning. With the right equipment, understanding of components, and practical experience, even beginners can leverage RTK GPS for a wide range of applications, from agriculture to construction and beyond.